Stroke Therapy Research. What works?
NeuroRehab Team
Friday, January 13th, 2023
Arm and HandElectrical StimulationHand Function SplintsMental PracticeMirror TherapyNeuroplasticityStroke Statistics

Every 2.1 seconds, someone in the world suffers a stroke. Stroke is the #1 cause of long-term disability worldwide. Globally, there are over 15 million stroke survivors. With respect to the United States, there are approximately 5.1 million stroke survivors alive today in the US. It is the third leading cause of death in USA and the numbers are expected to double by 2030.
Improve Results Following Stroke with These Simple Steps.
NeuroRehab Team
Monday, November 14th, 2022
Mental PracticeMirror TherapyNeuroplasticitypriming

Priming the Brain Works.
Better clinical outcomes following stroke are associated with interventions such as cortical priming resulting in increased excitability of the motor cortex (Catano et al).
Priming is a technique used to enhance the brain’s ability to re-balance the 2 hemispheres following a stroke. Priming interventions include invasive and non-invasive techniques and can be administered prior to or during therapy.
Stroke Survivors Should Look in the Mirror – Daily.
NeuroRehab Team
Friday, October 14th, 2022

Stroke survivors are beautiful and handsome heroes. But it’s not about vanity – it’s about recovery. Mirror Therapy (MT) is a critical intervention – yet vastly underutilized.
What You Need to Know About the Stroke Recovery Timeline
NeuroRehab Team
Wednesday, February 19th, 2020
Arm and HandContracture SplintElectrical StimulationHand Function SplintsMental PracticeMirror TherapyNeuroplasticityStretchingSubluxation Slings

You are eager to return to your normal life, so you are ready to learn more about the typical timeline for recovery after a stroke. Keep reading to get some answers to common questions:
- Am I going to get better after my stroke?
- How long is rehab after a stroke going to take?
- What can I do to help my stroke recovery?
Improve Functional Mobility With Lower Extremity Stroke Technology
NeuroRehab Team
Tuesday, December 26th, 2017
BalanceBody Weight SupportElectrical StimulationExercise AidsFoot Drop BraceLegLeg BikeMirror TherapyMobilityNeuroplasticity
One of the most common impairments resulting from stroke is paralysis, which can affect a portion or the entire side of the body. Problems with body posture, walking, and balance can be significant. A patient’s rehabilitation should start as soon as he or she is stable. That could be anywhere from a couple of days to a few weeks or longer. Established guidelines, as well as a huge body of literature, insist that the earlier therapy is initiated the better.
10 Must-Try Mirror Therapy Exercises
NeuroRehab Team
Thursday, October 5th, 2017
Electrical StimulationMirror Therapy

The principle of Mirror Therapy is the use of a mirror to create a reflective illusion of an affected limb in order to trick the brain into thinking movement has occurred. Mirror therapy allows the brain to be activated during the imitation movements and interact simultaneously with the motor neurons. For example, if you put your left hand behind a mirror and right hand in front, you can trick your brain into believing that the reflection of your right hand in the mirror is your left. You are now exercising your left hand in the brain!
Mirror Therapy Exercises for Improving Arm and Hand Function After Stroke
NeuroRehab Team
Thursday, April 21st, 2016
Arm and HandMental PracticeMirror TherapyNeuroplasticity
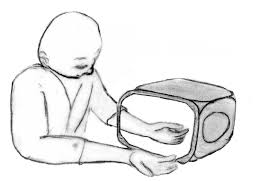
Mirror therapy, a treatment technique first described by V.S. Ramachandran for phantom limb pain following amputation, is a form of motor imagery in which a mirror is used to process visual feedback about motor performance of the unaffected body part as it performs various movements. It is primarily used to speed up and improve motor function after stroke and other neurological disorders.
Arm and Hand Recovery Following Stroke and Other Neurological Injuries
NeuroRehab Team
Friday, February 26th, 2016
Arm and HandArm BikeBiofeedbackElectrical StimulationExercise AidsHand Function SplintsMirror TherapyMobile Arm SupportsNeuroplasticityRoboticsSubluxation SlingsVirtual Reality
![]()
The latest research shows that the brain is capable of rewiring and adapting after stroke. Therefore, arm and hand recovery is more possible than previously thought. However, in order to improve function in the upper limb, the client must be willing to incorporate the affected side purposefully, functionally, and repeatedly. In addition to functional training, other beneficial strategies include strength training, mental imagery, robotics, and gravity compensation.
Below are the key takeaway’s that highlight the current thinking from the scientific community.

