Mirror Therapy Exercises for Improving Arm and Hand Function After Stroke
NeuroRehab Team
Thursday, April 21st, 2016
Arm and HandMental PracticeMirror TherapyNeuroplasticity
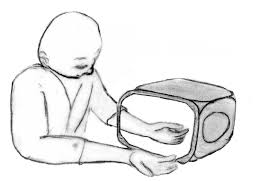
Mirror therapy, a treatment technique first described by V.S. Ramachandran for phantom limb pain following amputation, is a form of motor imagery in which a mirror is used to process visual feedback about motor performance of the unaffected body part as it performs various movements. It is primarily used to speed up and improve motor function after stroke and other neurological disorders.
How does it work?
Mirror theory is based on evidence that observation activates the same motor areas of the brain as execution. During mirror therapy, clients place their affected arm and hand inside the mirror box (to block their view of the affected side) and their unaffected hand and forearm in front of the mirror. The client is then directed to perform a movement with their unaffected hand and to simultaneously attempt to copy the movement with their hidden affected hand. The client should be looking at the image in the mirror while attempting to move the affected hand.

When looking into the mirror, the client observes the reflection of the unaffected limb positioned as the affected limb. This creates the illusion that both limbs are working normally. It is believed that by viewing the reflection of the unaffected arm and hand in the mirror that it may act as a substitute for the decreased or absent proprioceptive input (Foley et al. 2013). In addition, this strong visual cue from the mirror can therapeutically be used to improve motor performance and the perception of the affected limb (Rothgangel et al. 2013).
Strokes can cause significant neurological impairment, which may lead to a decline in functional independence and quality of life. Traditional therapy techniques focus on occupational and physical therapy exercises, often incorporating strength training and task-oriented drills. These treatment techniques can rebuild neuronal connections damaged by the stroke. Research shows that adding mirror therapy to the daily treatment regime can improve motor performance, therefore, ultimately leading to increased independence with daily living tasks.

