Further filter your results using the selections below...

While in therapy, it is not uncommon for patients and family members to enhance their rehab vocabulary from daily conversations with the clinical team. From the early moments of their arrival, they are immediately bombarded with clinical “whatchamacallits” from physicians, nurses, and therapists. Although the learning curve can be quite challenging, for many it is achievable thanks to Google and Yahoo.
Unfortunately, once the clinical jargon is finally mastered, the patients are preparing for their discharge date that is typically around the corner. It is not until their discharge week that they begin to have serious discussions with their occupational and physical therapists about what exercises to do at home and various equipment that might be needed.

Suffering a stroke is a life-changing event. The statistics show that many patients will struggle from long-term impairments well after discharge from the hospital. In addition, a majority of stroke survivors will require ongoing rehabilitation on an outpatient basis so continued progress can be made.
As if learning to adjust to a new life following an injury is not difficult enough, finding a good therapist can be challenging. Like every profession, some individuals are hard working, passionate and extremely knowledgeable about their respective industry, while others seem to live day-to-day in an alternate universe lacking basic skills, motivation and common sense. When your recovery is in the hands of a therapist, it is absolutely critical that you identify the best possible clinician that checks all of your boxes so maximum progress can be made.
![]()
One of the most common impairments resulting from stroke is paralysis, which can affect a portion or the entire side of the body. Problems with body posture, walking, and balance can be significant. Two thirds of the patients are unable to walk without assistance in the first week after stroke (Jorgensen HS et al. Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 1995). Approximately 35% of survivors with initial paralysis of the leg do not regain useful walking function (Hendricks HT et al. Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 2002). Although 65% to 85% of stroke survivors learn to walk independently by 6 months post stroke, gait abnormalities and poor endurance persists through the chronic stages of the condition (Wade DT et al. Scand J Rehabil Med, 1987).

A recent randomized trial by Yuzer et al., in the Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases 2017, investigated the effects of functional electrical stimulation of the wrist and finger extensor muscles of patients with chronic stroke who had spasticity of their wrist flexors.
Anyone who’s done physical or occupational therapy knows how hard it is not to cheat. The body wants to get back to work, and the easiest way to do that is to use the uninjured limbs to help out. The therapist is there to make sure it’s the injured limb that’s doing the work.
Intensive therapy can help people who have suffered a stroke recover motor function—even if the treatment begins a year or more after the stroke occurred. After a stroke, the brain and body can start recovering immediately and can show improvement up to six months afterward.
One of the most common impairments resulting from stroke is paralysis, which can affect a portion or the entire side of the body. Problems with body posture, walking, and balance can be significant. A patient’s rehabilitation should start as soon as he or she is stable. That could be anywhere from a couple of days to a few weeks or longer. Established guidelines, as well as a huge body of literature, insist that the earlier therapy is initiated the better.
A common impairment following stroke is called hemiparesis or one-sided (“hemi”) weakness (“paresis). Hemiparesis affects about 8 out of 10 stroke survivors, causing weakness or the inability to move one side of the body. One-sided weakness can affect your arms, hands, legs and facial muscles. Individuals with hemiparesis may have trouble performing everyday activities such as eating, dressing, and using the bathroom. Rehabilitation techniques, such as strengthening exercises, can help with speeding up your recovery.
Listed below are 10 exercise products that can help improve your strength following stroke.

The principle of Mirror Therapy is the use of a mirror to create a reflective illusion of an affected limb in order to trick the brain into thinking movement has occurred. Mirror therapy allows the brain to be activated during the imitation movements and interact simultaneously with the motor neurons. For example, if you put your left hand behind a mirror and right hand in front, you can trick your brain into believing that the reflection of your right hand in the mirror is your left. You are now exercising your left hand in the brain!
Activities of Daily Living (ADL) are impacted continuously for may stroke survivors that suffer from limited arm and hand function and movement. Research indicates that Biofeedback and Electrical Stimulation can result in improved mobility and functional use. Biofeedback combined with electrical stimulation (NMES or FES) can be an effective tool in reducing the symptoms of stroke, such as increasing strength and function.
Following a stroke or other neurological injury, multiple vision disorders can occur including the inability to recognize objects, color vision deficits and difficulty with perceiving various types of motion. Approximately 20% of patients experience permanent visual deficits (Romano JG. J of Neurol Sci. 2008).
According to the National Stroke Association, homonymous hemianopia, which is the loss of one half of the visual field in each eye, is the most common visual disorder. Most people who have vision loss after a stroke do not fully recover their vision. Thankfully, some recovery is possible. Treatment and outcomes will depend on the type of vision impairment and its cause.
Listed below are 7 Visual Motor Training Devices that are currently available on the market that can assist with improving recovery.
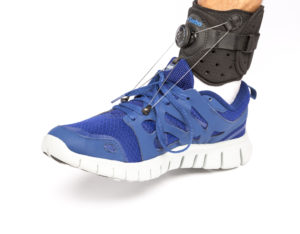
Whether you suffered a stroke, living with multiple sclerosis (MS) or experiencing another neurological disorder, experiencing Foot Drop can be quite a struggle. Finding the right support to maintain foot clearance when walking can be challenging at best. Areas of concern include size, comfort, durability and effectiveness.
Listed below are 5 comfortable “out-of-shoe” Foot Drop Braces that are currently available on the market. Although the below braces may be more comfortable to wear, it is important to realize that not everyone will qualify for these lower profile ankle supports. Individuals will need to consult with a healthcare professional to make the most appropriate choice for their needs.


It is not uncommon for individuals to experience decreased hand function and strength following a neurological injury such as stroke. Sadly, even after 6 months following stroke, over 60% of clients are still struggling to achieve full arm and hand recovery (Kwakkel et al., 2003). Moreover, the inability to actively open the hand for pre-grasp activities is a severe limitation for many stroke survivors. The impaired movements lead to decreased independence in leisure and self-care tasks (activities of daily living). Because this limited function is a difficult challenge, traditionally, clients were required to relearn new compensatory movement patterns and one-handed strategies so functional activities could be achieved.
The Stroke Hand and Upper Limb Clinic, offered by occupational therapists specializing in neurorehabilitation, provides an intensive (3 days, 6 hours per day) upper extremity treatment program for patients suffering from neurological impairments such as spasticity and weakness. The specialized stroke clinic, located in Charleston, SC is geared primarily towards clients that struggle with arm and hand function.

Listed below are various clinical product categories that you may have learned while in therapy. Feel free to click on any category to see a list of products that may be appropriate for your needs.

Studies have shown that stroke survivors are twice as likely to fall following a stroke and more than three times as likely as the general population to fall multiple times. About 40 percent of stroke survivors have serious falls within a year of their stroke.

It is true that recovering from a stroke will be an uphill battle for many, however, it is also accurate that the latest research findings regarding neuro recovery are more promising than ever before. How serious are you with embracing evidence into your practice? As a clinician, are you stuck using numerous theoretical-based treatment concepts that have not scientifically been proven to be effective?
Listed below are some of the common interventions supported by research that have shown positive results. How many of the below techniques are in your current therapy toolbox? If just a few, then why?

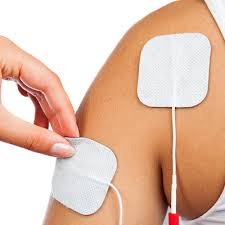
Electrical stimulation, also referred to as e-stim, NMES, or FES, can be an effective tool in reducing the symptoms of stroke, such as increasing strength and function. The success of one’s recovery using electrical stimulation will rely heavily on proper electrode placement.
Listed below are some key video examples of lower limb electrode positioning by Axelgaard. Click on the thumbnail below to visit the video link.
Neurological conditions can cause trouble with swallowing as a result of damage to the brain, spinal cord and nerves. This type of swallowing problem is called dysphagia. The most common conditions associated with dysphagia include stroke, head trauma, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy and motor neuron disease, but any neurological disease can cause dysphagia.
Edema is swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body’s tissues. Although edema can affect any part of your body, it’s most commonly noticed in the hands, arms, feet, ankles and legs. Edema occurs from a variety of reasons. For individuals who are inactive, a collection of fluid in the ankles and legs, fingers and hands can be seen. Individuals that are paralyzed after a neurological injury such as stroke, may have fluid collection just on the affected side.

It can be quite challenging caring for someone with a stroke. When a loved one is first hospitalized immediately after a stroke, families usually assist the hospital team with key personal information as well as convey patient care preferences and serve as the connection between the hospital staff and the patient. You suddenly become the patient’s voice and chief advocate.
What is it?
Constraint-induced movement therapy (CI, CIT, or CIMT) is a form of rehabilitation therapy that improves upper extremity function in stroke and other neurological injuries by increasing the use of their affected upper limb. The focus of CIMT is to combine restraint of the unaffected limb and intensive use of the affected limb. Types of restraints include a sling, a splint, a sling combined with a resting hand splint, a half glove, and a mitt. Determination of the type of restraint used for therapy depends on the required level of safety vs. intensity of therapy.
![]()
A new, non-biased website dedicated to assisting patients, families and health professionals with identifying appropriate neuro-rehab solutions and resources has recently launched. The directory is specifically designed for individuals with neurological injuries such as stroke, brain injury, cerebral palsy and spinal cord injury.

The latest research shows that the brain is capable of rewiring and adapting after stroke. Therefore, arm and hand recovery is more possible than previously thought. However, in order to improve function in the upper limb, the client must be willing to incorporate the affected side purposefully and repeatedly.
Electrical stimulation, also referred to as e-stim, NMES, or FES, can be an effective tool in reducing the symptoms of stroke, such as increasing strength and function. The success of one’s recovery using electrical stimulation will rely heavily on proper electrode placement.
Listed below are various clinical product categories that you may have learned while in therapy. Feel free to click on any category to see a list of products that may be appropriate for your needs.

Evaluating the impact of stroke rehabilitation requires the use of reliable, valid, and objective outcome measures. Despite consensus among nationally published guidelines recommending the use of valid and reliable assessment tools, the scientific community lacks direction regarding what outcome measures should be selected for particular evaluative needs. One measure that appears to have general acceptance and embraced by many neurorehabilitation specialists is the Action Research Arm Test (ARAT).

A stroke, or cerebrovascular accident (CVA), is the rapid loss of brain function(s) due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. When you have an ischemic stroke, there is an interruption, or reduction, of the blood supply. Eighty percent of all strokes occur due to ischemia. With a hemorrhagic stroke, there is bleeding in the brain. After about 4 minutes without blood and oxygen, brain cells become damaged and may die. When brain cells are damaged or die, the body parts controlled by those cells cannot function. The loss of function may be mild or severe and temporary or permanent. This depends on where and how much of the brain is damaged and how fast the blood supply can be returned to the affected cells.

There is strong evidence that repetitive task specific training techniques improve upper extremity function. Task training yields long lasting cortical reorginization specific to the corresponding areas being used. Traditional treatment interventions are based primarily on routine exercises and/or purposeful activities. For many patients, the road to recovery is long and difficult and clinicians are challenged with the daunting task of maintaining patient motivation and compliance while alleviating boredom. Computer based games and virtual reality have recently emerged as novel strategies to maintain motivation and compliance while providing the necessary repetitive training.
![]()
Improve Your Vision Recovery Techniques Now
Approximately 30% of all stroke patients suffer from post-stroke visual impairment (Sand KM. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 2013). Following a stroke or other neurological injury, various types of vision deficits can occur including the inability to recognize objects, color vision deficits and difficulty with perceiving various types of motion. Approximately 20% of patients experience permanent visual deficits (Romano JG. J of Neurol Sci. 2008).

A new stimulation device called the SaeboStim Micro is now available for neurological patients limited with arm and hand function. The SaeboStim Micro provides low-level sensory electrical stimulation to the arm and hand using a specialized Electro-Mesh Garment. The unique Electro-Mesh material is not only soft and comfortable to wear at rest, but also during activities. Clients suffering from impaired function, weakness and spasticity can benefit from the much-needed stimulation.

It is true that recovering from a stroke will be an uphill battle for many, however, it is also accurate that the latest research findings regarding neuro recovery are more promising than ever before. How serious are you with embracing evidence into your practice?
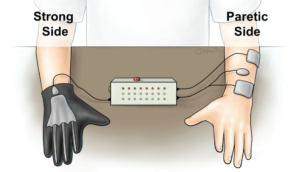
According to new research published in the American Heart Association journal Stroke, researchers at the MetroHealth System, Case Western Reserve University, and the Cleveland Functional Electrical Stimulation Center have developed a glove that allows patients be in control of the stimulation to their weak hand.

Damage to the brain after a stroke can cause many cognitive changes. Doing things that once were easy may now be hard. Problems with memory and thinking are very common after a stroke and most people will have some difficulties. After a stroke, cognitive rehabilitation can aid the mind just as physical therapy aids the body, according to Psych Central, an online mental health and psychology network. The purpose of cognitive therapy is to improve damaged mental abilities and language skills caused by a stroke.

One of the most common areas often affected by a neurological injury is the glenohumeral joint (i.e., shoulder). The shoulder complex is a very sophisticated and complicated joint in the body. It consists of 20 muscles, 3 bones, 3 joints, and 1 articulation. It has the greatest ROM of any joint in the body but at the expense of stability.

Are you caught up with the latest advances in neurorehabilitation? Find relevant stroke neuro courses below to be sure.
Find Leg and Mobility NeuroRehab Courses
Following an extensive search of 100’s of stroke rehabilitation products and programs, we have summarized the best available products currently on the market for stroke recovery. The products are organized into relevant categories list below. Feel free to click on any category to see a list of products that may be appropriate for your needs.

Stroke Recovery By The Numbers
Arm and hand recovery continues to be a major problem following neurological injury. According to scientific data, fifty-percent of stroke survivors are likely to regain some functional use of the upper limb (Broeks JG et al. Disabl and Rehabil, 1999).
Find Arm and Hand NeuroRehab Courses
Forty-one percent of all patients had limited hand use at 3 months and 45% at 18 months after stroke (Welmer AK et al. J Rehabil Med, 2008). At 6 months post stroke, some dexterity was found in 38% and complete functional recovery was seen in 11.6% of patients (Kwakkel G et al. Stroke, 2003).
The latest research shows that the brain is capable of rewiring and adapting after stroke. To improve function in the upper limb, the client must be willing to incorporate the affected side purposefully, functionally, and repeatedly. In addition to functional training, other evidence-based strategies include strength training, mental imagery, robotics, and gravity compensation.
The American Occupational Therapy Association's (AOTA's) Approved Provider Program (APP) assists occupational therapy practitioners (OTPs) and state licensing boards to ensure professional development activities reflect evidence-informed, occupation-centered practice. AOTA Approved Providers demonstrate they have the systems, policies, procedures and educational practices in place to adhere to the APP Guidelines and Criteria.

The above courses are evidence-based courses that review the latest information when it comes to stroke recovery. To search for stroke rehab exercise tools, visit here get started.
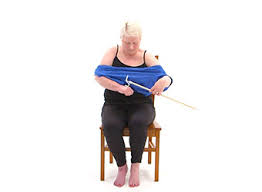
Occupational therapists advise and counsel clients on strategies to increase functional independence and improve quality of life. Many occupational therapists struggle with knowing how to demonstrate adaptive strategies to clients who have suffered loss of one hand or loss of function of one hand to complete functional activities.
Now more than ever, occupational, physical and speech therapists are relying on evidence-based treatment to provide maximum outcomes for clients suffering from stroke and other neurological injuries. Get up-to-date with the latest advances in stroke/neuro treatment by enhancing your skills through continuing education courses.
Listed below are links to online training categorized into key groups. Feel free to click on the link to learn more about available courses.

Individuals suffering from stroke may have difficulty with activities of daily living (ADL) such as grooming, dressing, managing a household, and with performing familiar roles (e.g., parent, spouse, employee). According to the American Occupational Therapy Association (AOTA), occupational therapy practitioners address the physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges brought on by a stroke, and they can help stroke survivors engage in the things they want and need to do. The following tips are from occupational therapy practitioners who work with people recovering from a stroke.

Most people who have decreased vision or double vision after a stroke do not fully recover. Some recovery is possible and it usually happens in the first few months after a stroke.

Help patients, families, and clinicians make the best decisions based on your feedback.
Excitement is building with new web-based platform, neurorehabdirectory.com, a free online resource dedicated to assisting stroke patients, families and health professionals with identifying appropriate stroke therapy products and programs. Traditional online medical websites are either out-of-date, difficult to navigate or sponsored by manufacturers. Neurorehabdirectory.com free web-based platform was developed to help individuals seamlessly search for total body stroke rehab treatment solutions and programs in an impartial way.

The National Institute of Neurological Disorders defines foot drop, also known as dropped foot or drop foot, as “the inability to raise the front part of the foot due to weakness or paralysis of the muscles that lift the foot.” Consequentially, people who have foot drop scuff their toes along the ground; they may also bend their knees to lift their foot higher than usual to avoid the scuffing, which causes what is called a “steppage” gait.
Amit Kumar, Occupational Therapist, LS Life Skills Therapy Services Inc., Surrey, BC
Every stroke survivor’s impairment is unique. By doing regular functional activities and exercises, you can increase your quality of movement and independence in all stages following stroke. Activity may be too easy or too hard depending on the extent of impairment and function. Your occupational therapist can help you develop a daily activity and exercise program appropriate for you. Activities and exercises to improve your hand function should be simple and done at home at any time.

Electrical stimulation, also referred to as e-stim, NMES, or FES, can be an effective tool in reducing the symptoms of stroke, such as increasing strength and function. The success of one’s recovery using electrical stimulation will rely heavily on proper electrode placement.
Listed below are some key video examples of upper limb electrode positioning by Axelgaard. Click on the thumbnail below to visit the video link.